Set Bedrock integration
What is Bedrock?
Amazon Bedrock is a fully managed service that offers a choice of high-performing foundation models (FMs) from leading AI companies like AI21 Labs, Anthropic, Cohere, Meta, Mistral AI, Stability AI, and Amazon itself through a single API, along with a broad set of capabilities that allow you to build generative AI applications with security, privacy, and responsible AI.
You can interact with the Amazon Bedrock API through the AWS Software Development Kit (SDK) or the AWS CLI, and you can use Bedrock’s native features to build your own RAG knowledge bases, agentic workflows, and guardrails. Integrating Bedrock with OPEA allows you to access an even larger selection of foundation models, as well as leverage the power of Bedrock’s features in combination with OPEA.
How Does the Architecture Change?
Future integrations with OPEA will unlock the power of Bedrock features as well as Titan Embedding models, but for this module we’ll concentrate exclusively on the LLM’s. Thanks to the interchangeability offered by OPEA, most of the components from the default ChatQnA example (Module 1). The TGI service (Hugging Face) is now replaced by bedrock container that can be seamlessly integrated into a new deployment. The architecture closely resembles the ChatQnA with the new component:
chatqna-bedrock
In this deployment when you access the UI the message is sent to the backend bedrock container which receives responses from Amazon Bedrock.
We’ve used the bedrock Kubernetes namespace to separate out the pods and services pertaining to the Bedrock deployment. When you use kubectl and other Kubernetes commands in the below examples, be sure to qualify the command with -n bedrock.
Deploying ChatQnA Using Amazon Bedrock LLMs
For this lab, we’ve created a changeset with the full parallel deployment of the ChatQnA example in the same Kubernetes cluster you’ve been using. The following command will deploy pods to the cluster within the “bedrock” namespace that are identical to the original ChatQnA pods, except with Bedrock models instead of TGI.
aws cloudformation execute-change-set --change-set-name bedrock-change-set --stack-name OpeaBedrockStack
Activating the Model
This module works with just about any text-generation LLM supported by Bedrock, but for the purposes of this lab we’ve used the Anthropic Claude Haiku 3 model. So while you’re waiting for the change set to deploy, let’s go activate our model in the Bedrock console:
- Switch to the
us-west-2region, you could test on other regions but usually us-west has more availabity:
- Go to Amazon Bedrock:
- Go to the
model accesstab:
- At the top of the screen, click on the button that says
Enable Specific Models
- Select
Claude 3 Haiku
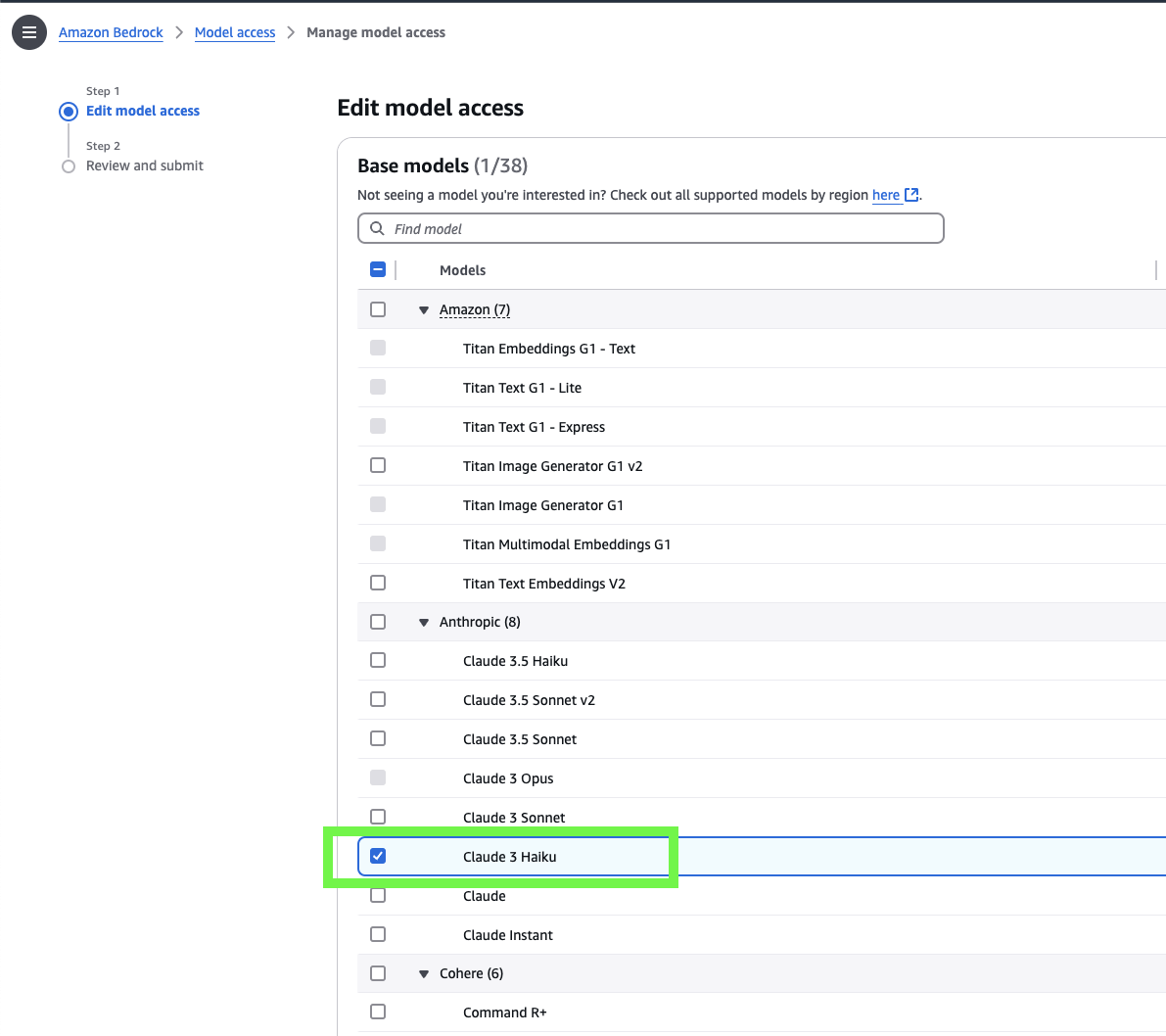
It may take a minute or two for the access to be granted, but don’t worry it won’t take much longer than that.
- Once you’ve confirmed that model access has been granted, switch back to your region where your EKS cluster is located.
Confirming Deployment
Now let’s confirm that our Bedrock deployment is complete. You can onitor the state of the Bedrock pods using the kubectl command:
kubectl get pods -n bedrock
…to get output like this:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
chatqna-bedrock-deployment-5b697d758-7gsdr 1/1 Running 0 28s
chatqna-chatqna-ui-deployment-7fc549b9b5-jhntn 1/1 Running 0 28s
chatqna-data-prep-deployment-c47d67f89-lplq8 1/1 Running 0 28s
chatqna-deployment-7db8bf47fb-mjcxr 1/1 Running 0 28s
chatqna-nginx-deployment-656bc748d4-4wqjz 1/1 Running 0 28s
chatqna-redis-vector-db-deployment-65cc8d87b-smqrb 1/1 Running 0 28s
chatqna-retriever-usvc-deployment-55f5676745-5d5cj 0/1 Running 0 28s
chatqna-tei-deployment-85d9484bf7-2l7jr 1/1 Running 0 28s
chatqna-teirerank-deployment-589dd896d9-xjvmp 1/1 Running 0 28s
It can take several minutes for Bedrock to fully initialize and be available. Only continue when you see the chatqna-bedrock-deployment pod in the Running state.
You are now able to use Amazon Bedrock in your environment.