Deploy Guardrails
Why would you need guardrails?
As AI becomes more integral in applications, ensuring reliable, safe, and ethical outcomes is critical. Guardrails in AI systems, especially those interacting with users or making decisions, help maintain control over responses, avoid unintended behaviors, and align output with set goals and standards. Without guardrails, AI models might generate unsafe or biased content, make inappropriate decisions, or mishandle sensitive data.
Implementing guardrails allows you to:
- Enhance User Safety – By controlling responses, you reduce the risks of harmful outputs in AI interactions.
- Maintain Compliance – As privacy and safety regulations grow, guardrails ensure your applications remain within legal boundaries.
- Optimize Accuracy – Guardrails can improve the quality of AI output, reducing error rates and providing more reliable performance.
Ultimately, guardrails allow you to harness AI’s benefits while mitigating risks, ensuring a more secure and trustworthy user experience.
How does the OPEA architecture change?
Thanks to the interchangeability offered by OPEA, most of the components from the default ChatQnA example (Module 1) remain unchanged, with the addition of a few that can be seamlessly integrated into a new deployment. The architecture closely resembles the ChatQnA setup without guardrails, with two additional components:
chatqna-tgi-guardrailschatqna-guardrails-usvc
The chatqna-tgi-guardrails microservice launches a TGI server using the meta-llama/Meta-Llama-Guard-2-8B model. This model acts as a real-time filter to ensure that all queries processed through the ChatQnA pipeline adhere to defined safety protocols.
The chatqna-guardrails-usvc microservice serves as the operational endpoint analyzer (OPEA), evaluating user queries to determine if they request content deemed unsafe by the model.
Deploying ChatQnA guardrails
Kubernetes enables the isolation of development environments through the use of multiple namespaces. Since the pods for the ChatQnA pipeline are currently deployed in the default namespace, you will deploy the guardrails in a separate namespace guardrails, to avoid any interruptions.
If you have been logged out of your CloudShell, click in the CloudShell window to restart the shell, or click the icon in the AWS Console to open a new CloudShell
- Go to your CloudShell and deploy the ChatQnA-Guardrails ClourFormation template into your EKS Cluster
aws cloudformation execute-change-set --change-set-name guardrails-change-set --stack-name OpeaGuardrailsStack
The manifest for ChatQnA-Guardrails can be found in the ChatQnA GenAIExamples repository, and the instructions for deploying it manually can be found here. The instructions you’re using in this workshop use AWS CloudFormation templates created by the AWS Marketplace EKS package.
- Verify the new namespace was created
kubectl get namespaces
:::
You will see the `guardrails` namespace
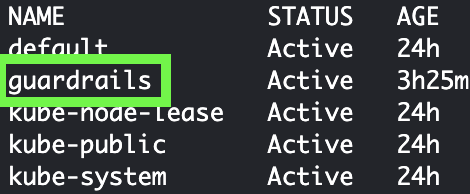
3. Check pods on the `guardrails` namespace. It will take a few minutes for the models to download and for all the services to be up and running.
Run the following command to check if all the services are running:
:::code{showCopyAction=true language=bash}
kubectl get pods --namespace guardrails
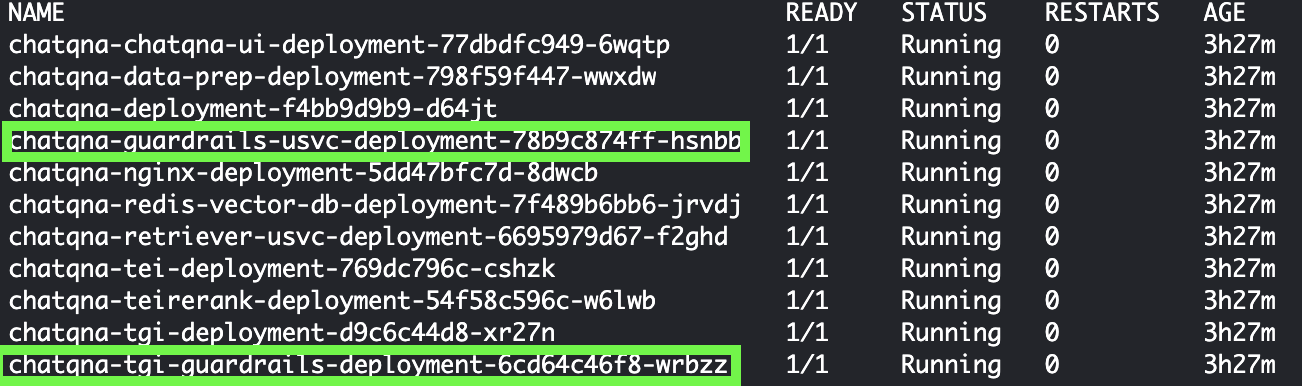
Wait until the output shows that all the services including chatqna-tgi-guardrails and chatqna-guardrails-usvc are running (1/1).
- Verify the deployment is done verifying the new load balancer on your managment console
Wait 5 minutes for the load balancer to be created.
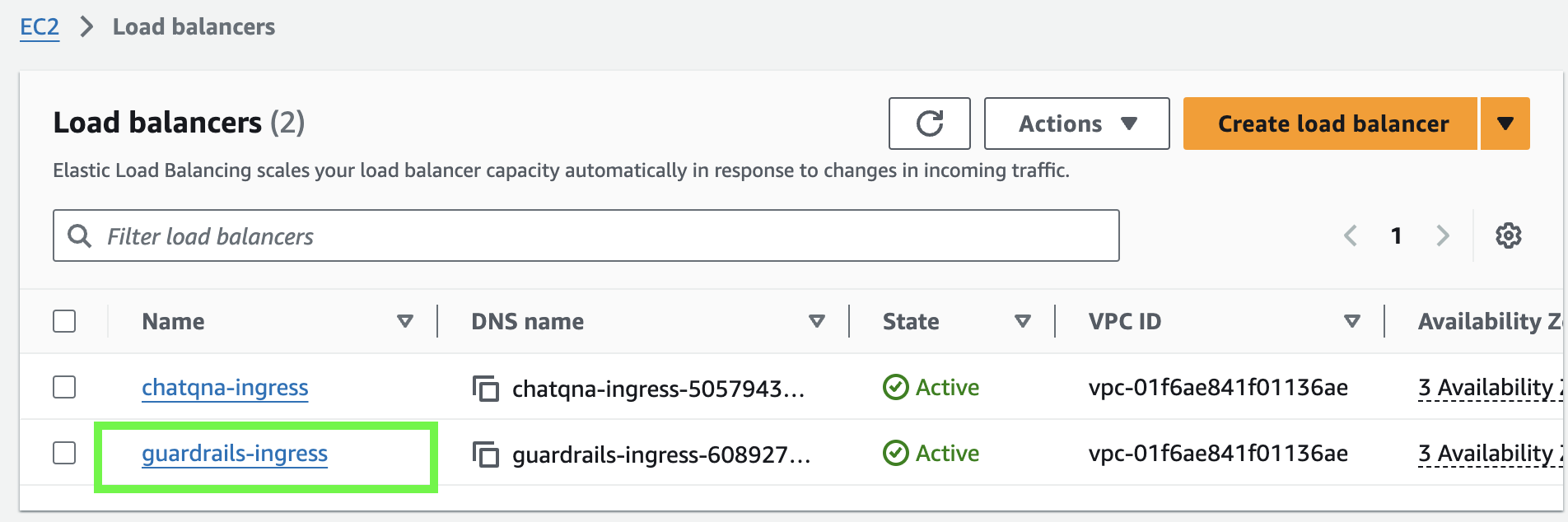
By checking that both the load balancer and pods are running, we can confirm that the deployment is ready and start testing the behavior.